Resource Center
Articles
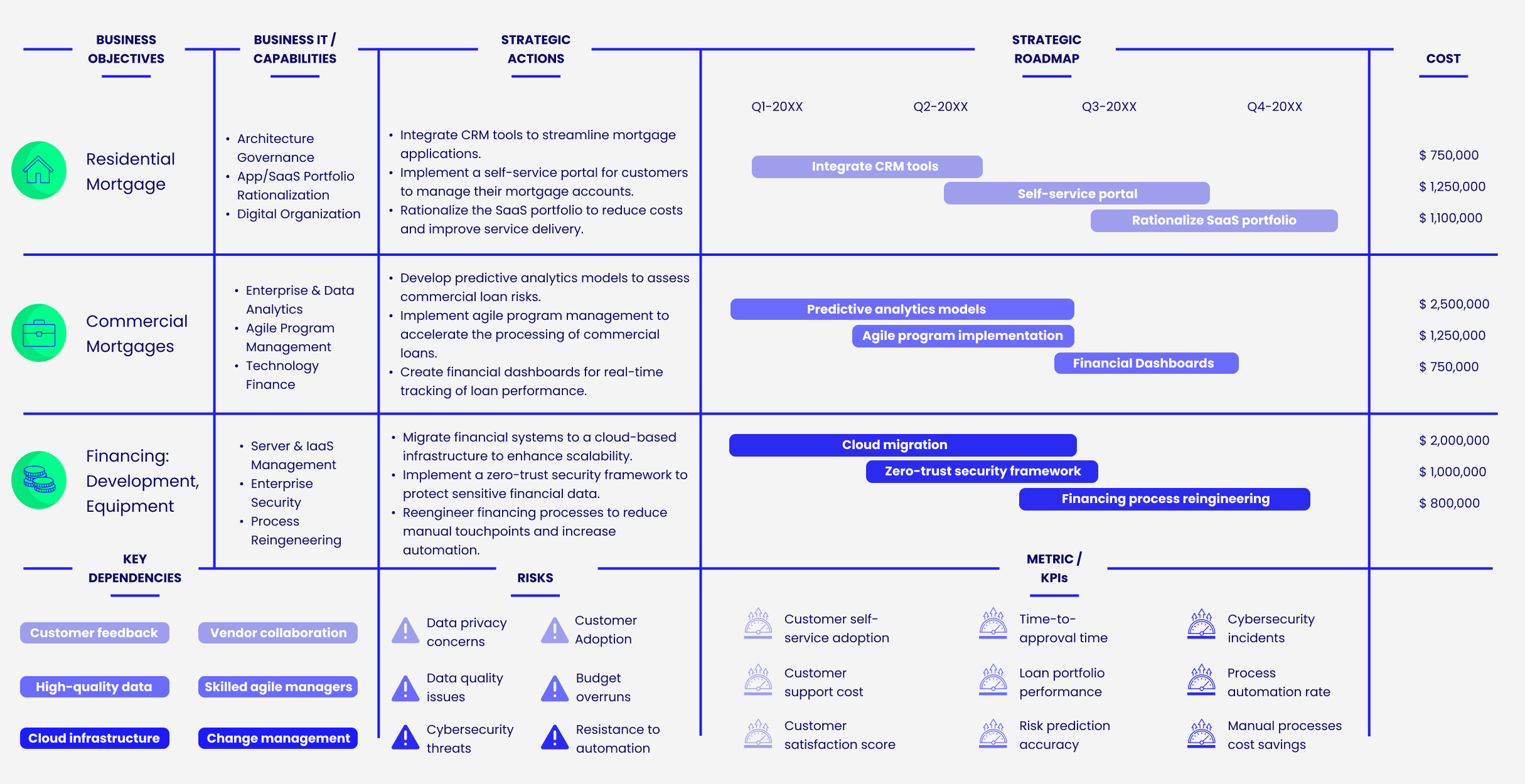
Lenders Transformation Playbook: Bridging Strategy and Execution
AI’s Mid-Market Makeover in Financial Services

Mid-sized financial services institutions (FIs) are facing significant challenges during this period of rapid technological change, particularly with the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). As customer expectations grow, smaller banks and lenders must stay competitive and responsive. Canada’s largest financial institutions are already advancing in AI, while many others remain in ‘observer’ mode, hesitant to invest and experiment. Yet, mid-sized FIs that adopt the right strategy have unique agility, allowing them to adapt swiftly and efficiently to technological disruptions—even more so than their larger counterparts.
Blanc Labs Welcomes Tom Purves as a Leader in Payments and Product Innovation

Blanc Labs has teamed up with industry expert, Tom Purves to bring leadership and expanded capabilities to our clients as developments in real-time payments capabilities evolve the market.
Why Banks and Credit Unions Should Pick Technology Vendors with SOC 2 Type II Certification

Achieving SOC 2 Type II compliance is crucial for vendor partners in the financial sector, ensuring robust security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Discover why technical leaders are prioritizing SOC 2 Type II compliance to stay ahead in an increasingly regulated industry.
How Open Banking Will Empower Small Businesses in Canada

With 85% of business owners seeking faster access to capital in today’s challenging economy, Open Banking offers a way out. This guide explores how it addresses issues like high inflation and slow lending processes, aiding small businesses in navigating the evolving landscape.
Align, Assemble, Assure: A Framework for AI Adoption

An in-depth guide for adopting and scaling AI in the enterprise using actionable and measurable steps.
Case Studies
Process Improvement and Automation Support the Mission at Trez Capital 🚀

Trez distributes capital based on very specific criteria. But with over 300 investments in their portfolio, they process numerous payment requests and deal with documents in varied data formats. They saw an opportunity to enhance efficiency, improve task management, and better utilize data insights for strategic decision-making.
Shannex Adopts Automation to Revolutionize its Employee Experience

Shannex has partnered with Blanc Labs to develop a workflow that leverages Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to improve coordination of task between departments, track onboarding activities and timelines, and manage employee access to new employees or when their role changes. This innovative partnership is being supported by the Coordinated Accessible National (CAN) Health Network.
Low-Code Tools and Automation Power Minor Ailments Program for Pharmacists
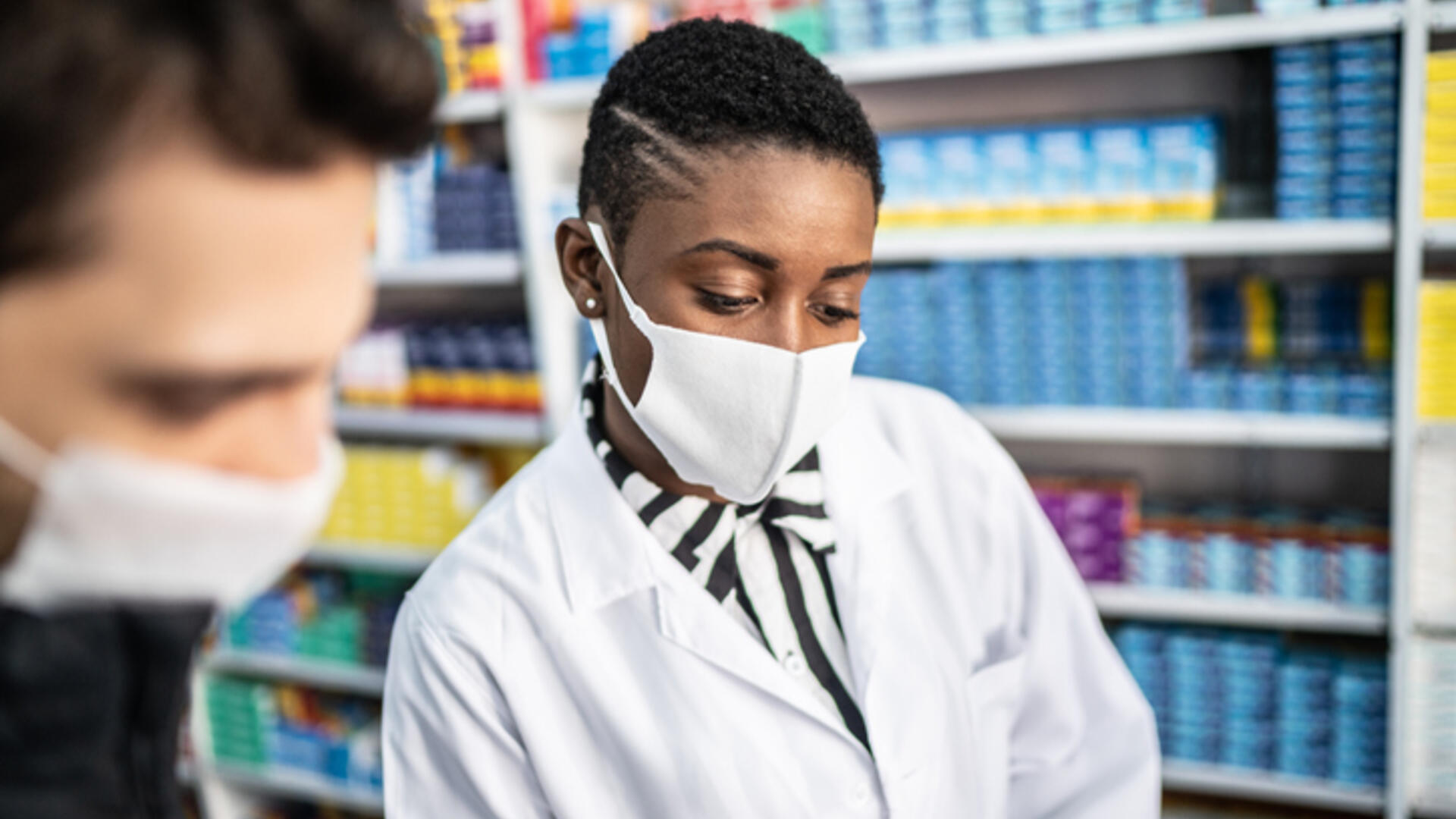

Blanc Labs teamed up with Daylight Automation (acquired by Quadient) to overhaul the process pharmacists use to assess and treat minor ailments, at a critical inflection point for Canadians to efficiently access healthcare services.
Company News
Blanc Labs Welcomes Tom Purves as a Leader in Payments and Product Innovation

Blanc Labs has teamed up with industry expert, Tom Purves to bring leadership and expanded capabilities to our clients as developments in real-time payments capabilities evolve the market.
Blanc Labs Welcomes Two New Leaders to Advance AI Innovation and Enhance Tech Advisory Services for Financial Institutions Across North America

Blanc Labs and TCG Process have partnered to transform lending operations with innovative automation solutions, using the DocProStar platform to enhance efficiency, compliance, and customer satisfaction in the Canadian lending market.
Blanc Labs Partners with TCG Process to Integrate their Automation and Orchestration Platform and deliver Advanced Intelligent Workflow Automation to Financial Institutions

Blanc Labs and TCG Process have partnered to transform lending operations with innovative automation solutions, using the DocProStar platform to enhance efficiency, compliance, and customer satisfaction in the Canadian lending market.
Meet David Liu: COE Lead, Process Improver, and Ramen Aficionado

Meet our new BPI CoE Lead, David Liu! Learn about how he plans to craft efficient processes for enterprise customers and what inspires him to innovate.
2023 Fall Economic Update on Consumer-Driven Banking 🥳

Blanc Labs provides their POV on the recent Open Banking Update by the Federal Government.
Shannex Announces Partnership with Canadian-based Blanc Labs to Improve Employee Experience and Resident Care

Shannex, a family owned and operated organization is partnering with Canadian health care technology company, Blanc Labs, to deploy automated processes to improve employee experience.
Financial Services
AI’s Mid-Market Makeover in Financial Services

Mid-sized financial services institutions (FIs) are facing significant challenges during this period of rapid technological change, particularly with the rise of artificial intelligence (AI). As customer expectations grow, smaller banks and lenders must stay competitive and responsive. Canada’s largest financial institutions are already advancing in AI, while many others remain in ‘observer’ mode, hesitant to invest and experiment. Yet, mid-sized FIs that adopt the right strategy have unique agility, allowing them to adapt swiftly and efficiently to technological disruptions—even more so than their larger counterparts.
Why Banks and Credit Unions Should Pick Technology Vendors with SOC 2 Type II Certification

Achieving SOC 2 Type II compliance is crucial for vendor partners in the financial sector, ensuring robust security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Discover why technical leaders are prioritizing SOC 2 Type II compliance to stay ahead in an increasingly regulated industry.
How Open Banking Will Empower Small Businesses in Canada

With 85% of business owners seeking faster access to capital in today’s challenging economy, Open Banking offers a way out. This guide explores how it addresses issues like high inflation and slow lending processes, aiding small businesses in navigating the evolving landscape.
Align, Assemble, Assure: A Framework for AI Adoption

An in-depth guide for adopting and scaling AI in the enterprise using actionable and measurable steps.
BPI in Banking and Financial Services in the US & Canada

Banking and financial services are changing fast. Moving from old, paper methods to new, digital ones is key to staying in business. It’s important to think about how business process improvement (BPI) can help.
Business Process Improvement vs Business Process Reengineering

Business process improvement vs. reengineering is a tough choice. In this guide, we help you choose between the two based on four factors.
Healthcare
Shannex Adopts Automation to Revolutionize its Employee Experience

Shannex has partnered with Blanc Labs to develop a workflow that leverages Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to improve coordination of task between departments, track onboarding activities and timelines, and manage employee access to new employees or when their role changes. This innovative partnership is being supported by the Coordinated Accessible National (CAN) Health Network.
Shannex Announces Partnership with Canadian-based Blanc Labs to Improve Employee Experience and Resident Care

Shannex, a family owned and operated organization is partnering with Canadian health care technology company, Blanc Labs, to deploy automated processes to improve employee experience.
Low-Code Tools and Automation Power Minor Ailments Program for Pharmacists

Blanc Labs teamed up with Daylight Automation (acquired by Quadient) to overhaul the process pharmacists use to assess and treat minor ailments, at a critical inflection point for Canadians to efficiently access healthcare services.
Healthcare Interoperability: Challenges and Benefits
Partner News
Blanc Labs Welcomes Tom Purves as a Leader in Payments and Product Innovation

Blanc Labs has teamed up with industry expert, Tom Purves to bring leadership and expanded capabilities to our clients as developments in real-time payments capabilities evolve the market.
People
Meet David Liu: COE Lead, Process Improver, and Ramen Aficionado

Meet our new BPI CoE Lead, David Liu! Learn about how he plans to craft efficient processes for enterprise customers and what inspires him to innovate.
Team Member Spotlight – Noel John, VP of Client Engagement and Delivery
Podcasts
Innovation Is The Key To Digitally Transform Financial Services
Webinars
Whitepapers
Open Banking Technology Architecture Whitepaper

We’ve developed this resource to help technical teams adopt an Open Banking approach by explaining a high-level solution architecture that is organization agnostic.
Winning the Open Banking Race: A Challenger’s Path to Entering the Ecosystem Economy

Learn about the steps you can take in forming an open banking strategy and executing on it.
From Chaos to Clarity: Achieving Operational Excellence through Business Process Improvement

Discover transformative insights and strategies to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and drive success.