by Bob Paajanen and Steven Chung
With the urgent need to catch up with FinTechs and appease customers, there is a lot of discussion today around digital transformation in banks and how technology can improve both the customer experience and the bottom line. The word API is thrown around, but few understand the tangible impact of how APIs can improve your bank. In this article, we break down what APIs can do and the areas in which they can significantly change the ways in which banks operate.
What is an API?
An API or Application Programming Interface allows disparate systems to communicate with one another. Think of APIs as waiters at a restaurant—they take your order and relay that order to the kitchen. The kitchen prepares your order, and the waiters bring it back to you. The waiter here is a middleman that relays important information that is within the framework of the menu (defining what information should be shared) in a format that is understood by the kitchen (structured data).
The most common examples of APIs include “login using Facebook” or “login using Google” which use APIs to connect your Fb and Google accounts to a third-party website.
The use of APIs increases flexibility, increases efficiencies and therefore improves the user experience.
What are banking APIs?
Banking APIs are specific to banking software. Since the pandemic, the demand for APIs has grown as customers expect real-time 24/7 support across all banking functions. Using APIs can allow the bank’s systems to talk to one another thereby providing the customer with a unified and seamless banking experience.
The use of banking APIs is up from 35% in 2019 to 47% in 2021 and another 25% of banks and credit unions plan to invest in APIs by 2022.
Using APIs not only connects legacy systems to one another but gives financial institutions the opportunity to reimagine how their operating model works, what the customer journey should look like and how they would like to interact with customers. Indeed, the use of APIs today, according to PYMNTS, could be compared to getting the “proverbial plumbing in place to enable new digital experiences.”
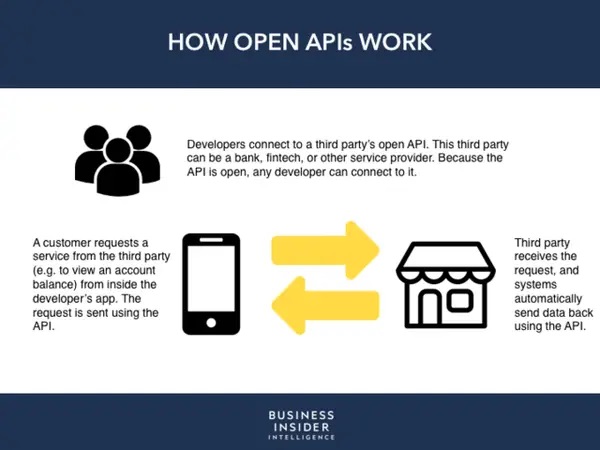
APIs and the future of Open Banking
Open banking is a system where banks enable their financial data to be securely accessible to third parties with the use of APIs. Using APIs gives financial institutions access to new banking technologies such as digital lending, online mortgage approvals, digital payments, account opening, engagement tools, analytical tools and a host of other functionalities, while also empowering customers to have more control over their data.
What can APIs do for your bank?
There are many types of APIs created for a variety of functions. In this article, we will focus on four of the most common types of banking APIs and how they can help in your digital transformation and modernizing efforts. These are:
- Integration
- Connectivity
- Platform Banking
- Innovation
Integration
Banking systems set up even five years ago are now considered legacy systems. Such legacy systems don’t usually communicate well with newer technologies. Failure to keep up with the consumer or regulatory demands of today may render the bank obsolete. This is where APIs come in. Instead of replacing legacy systems—a time-consuming and expensive process—APIs can help legacy systems communicate with new software at a fraction of the cost and twice the speed. A good example of APIs integrating banking systems would be providing a branch locator (using mapping software like Google Maps) on the bank’s mobile app.
With advancements in technology and frequently updated regulatory requirements, integrating legacy systems with newer technologies is no longer a choice but a necessity.
Connectivity
As services such as personal financial management become more automated across various functions within the bank, there is a growing need for better governance of user data, including customer checking and credit history.
Because APIs also regulate the information that they share between systems, they can filter out relevant information to a third party without disclosing every detail. They can also time how long the information will be available to a third-party program. For example, credit history may be available for only 30 days.
APIs available today, especially REST APIs(or web-based APIs), are lightweight, faster, more scalable, and offer real-time connectivity, making them a perfect use case for mobile applications.
Platform Banking
Many non-bank businesses such as FinTechs today opt for the banking-as-a-platform strategy, where APIs are used to connect the non-bank business to a bank. With the use of APIs the non-bank business can use the bank’s license and regulatory framework, thereby offering banking services without being banks themselves. This means lower operations costs, which they can pass on to the customer in the form of lower fees and better rates. Banks on the other hand can take advantage of the newer technologies offered by the FinTechs to improve their service offerings without having to build them themselves.
An example of this is Tangerine Bank, a no-branch “bank” that offers banking services like savings and checking accounts using Scotiabank’s banking license to operate. APIs allow seamless, real-time connectivity for Tangerine customers, allowing them to access their banking information on their mobile app.
Innovation
The ability to plug-and-play innovative technologies means that banks can now offer a variety of new products while creating better efficiencies at the back end. Using APIs, banks can circumvent an overhaul of their legacy systems, improving bits and pieces at a time. This will save banks both money and time. APIs also allow banks to integrate products and services in a modular way. This gives them a wider choice of vendors, and with that comes better control of price, quality, and delivery.
Banks need not always depend on third parties to add on new products and services. If they decide to go their modernization route themselves, they can use APIs to standardize the process and add tools without making drastic changes to the underlying system—something that most banks prefer.
APIs can also help connect one banking system to another. For example, an API can connect the lending workflow with a customer’s personal banking workflow. This connection can provide better efficiencies, reduce manual work, and improve employee satisfaction. APIs can also integrate automation tools such as end-to-end journal entries, loan document processing, and report creation on top of legacy systems, saving time and cost. A 2019 report by Accenture predicted that banks would see a productivity gain of US$ 59 billion by 2025 thanks to automation. This number is probably higher in the context of the pandemic, which forced banks to automate and modernize their processes even more aggressively.
Current Challenges with API integration
While many banking institutions recognize the benefits of APIs, integrating them into the banking system is not without its challenges. This is especially so when you have multiple teams across geographies using a variety of API tools and vendors. This leads to duplication of efforts, further complicates the system and therefore leads to a loss in productivity. Using the right API platform can take care of these issues while giving the additional benefit of security and governance.
Integrate APIs in your banking system with Blanc Labs
APIs offer an exciting future for banks. It is imperative that banks take advantage of new technological products and services and leverage open banking, so they are not left behind in the race with FinTechs and other competitor banks.
Blanc Labs offers APIs that unify all ledgers and functions so that banks can get a true 360-degree view of their customers and help banks upgrade systems to meet regulatory standards.
Book a demo or discovery session with Blanc Labs to learn about the impact of our API solutions for banking.